Along with terms like crypto, blockchain, and the metaverse, Web 3.0 is a major buzzword in the tech world. It’s about creating a new internet, promising a revolution similar to Web 2.0. But what exactly is Web 3.0, and what does it do? Is it just another use of blockchain, a scam, or something completely different? How close are we to making it real? And can it actually happen? Let’s explore the key questions about today’s web technologies and digital assets.
What Is Web3 (or Web 3.0)?
Web3, also known as Web 3.0 or “The Semantic Web,” is the next big step for the internet. It’s not just about new looks or features; it changes how we interact with, understand, and create online content. This new version of the web aims to be smarter, more decentralized and focused on users, moving away from the current centralized internet model.
Web 3.0 is still being developed, and it’s a tough job. Many projects and developers are excited about it, but it’s hard to put into practice. Unlike other tech advances like language models or cryptocurrency exchanges, Web 3.0 needs lots of people to get on board before it can truly happen.
Key Features of Web 3.0
- Ubiquity: Web 3.0 aims to provide a seamless online experience across all devices, from smartphones and computers to wearable gadgets. This means your web experience will be consistent and personalized no matter how you access it, making the internet available to everyone, everywhere.
- Semantic Web: The core of Web 3.0 is the Semantic Web, which understands the meaning behind content, not just the text and images. This allows for better search results, more relevant content suggestions, and a smoother user experience. It uses semantic metadata to provide context to the content.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI will be integral to Web 3.0, enhancing user experiences through smart chatbots, advanced recommendation systems, and other AI-driven features. This will make interactions more interactive and tailored to individual needs.
- Spatial Web and 3D Graphics: Web 3.0 will be immersive, thanks to advancements in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR). Websites and apps will evolve from flat designs to engaging 3D spaces, offering a richer, more engaging experience.
- Decentralization and Blockchain: One of the most revolutionary aspects of Web 3.0 is its move towards decentralization. Blockchain technology will play a key role, in providing data transparency, security, and independence from central authorities. This shift away from centralized control is what makes the decentralized internet so innovative.
How Will Web 3.0 Work?
In the early days of the internet, known as Web 1.0, websites were mostly static and allowed for little interaction. Web 2.0 introduced more interactive and social websites but relied heavily on centralized servers and databases. Web 3.0 is set to transform this model by using decentralized networks, offering users more control and privacy.
Web 3.0 will use peer-to-peer networks instead of centralized servers, meaning no single organization will control the data. This shift to decentralized data storage will ensure that information is not held by one central entity, enhancing security and privacy. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will play a crucial role in Web 3.0, making content delivery smarter and more intuitive. Unlike Web 2.0, where users manually add content, Web 3.0’s AI will understand and process content automatically, creating a more responsive web experience.
Governance of online communities could shift to Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs), which are self-regulating groups without central leadership, allowing for more democratic decision-making. Financial transactions will transition from traditional banks to blockchain-based platforms, making transactions more secure and eliminating the need for intermediaries.
With the growth of the internet, Web 3.0 will need more IP addresses than what Web 1.0 and 2.0 used. IPv6 will provide a vast number of addresses, overcoming the limitations of the older IPv4 system. Overall, Web 3.0 will be a smarter, more secure, and decentralized version of the Internet, giving users greater control and making online interactions more efficient and personalized.
Key Applications of Web 3.0
One major application of Web 3.0 is the metaverse, a virtual realm that acts like a 3D internet, mirroring the real world. Users can explore this space using computers, phones, or VR/AR headsets. Unlike the centralized approach of companies like Meta (formerly Facebook) and Google, Web 3.0 envisions a decentralized metaverse that values open-source development, interoperability, and fair rewards for creators. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) will be crucial in this space, representing unique digital assets. With proper development, the metaverse could revolutionize social networks as we know them.
Blockchain gaming is another key application, highlighted by the success of games like Axie Infinity and the play-to-earn model. Despite some challenges, combining gaming with decentralized technologies has the potential for significant growth, especially with a focus on enhancing the player experience.
The creator economy will benefit from Web 3.0 by allowing creators to connect directly with their audiences, bypassing intermediaries like YouTube or Spotify. This ensures fairer revenue distribution and makes it easier to create and monetize large-scale user-generated content. New social media platforms in Web 3.0 will streamline this process, giving creators more control and earnings.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) represent a new organizational structure where smart contracts enable self-governing entities that operate beyond geographical boundaries. This could lead to more democratic and efficient ways of managing groups and businesses.
Decentralized finance (DeFi), which saw significant growth in mid-2020, enables cryptocurrency users to invest, borrow, lend, trade, and stake crypto assets without needing permission. Despite security issues like hacks and scams, DeFi presents Web 3.0 with the opportunity to include billions of users who are underserved by traditional financial institutions.
Finally, blockchain technology implementation in Web 3.0 has many real-world applications, such as improving supply chain management. It simplifies the integration of blockchain networks into a company’s data management or operational processes, making these systems more efficient and secure.
What Is Web 2.0?
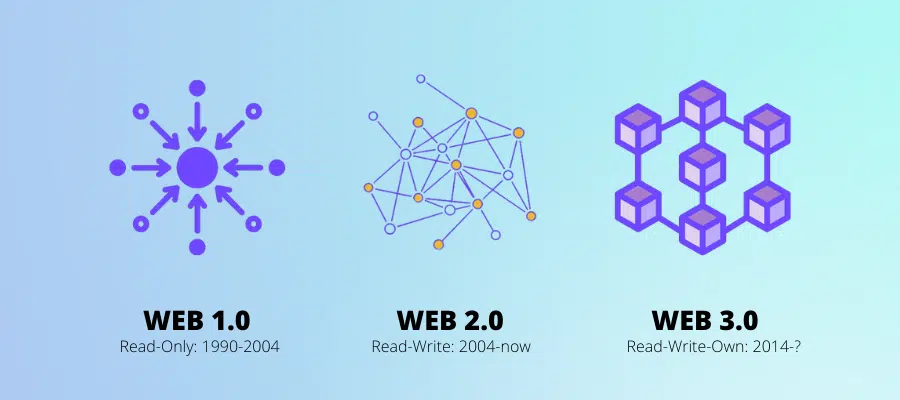
Web 2.0 is the phase of the internet we are currently experiencing, marked by the rise of social media and the democratization of content creation. Unlike the earlier Web 1.0 era, where users were passive consumers of content created by tech companies, Web 2.0 allows anyone to create, upload, and share content. This shift has led to the internet being called the “social web.”
In Web 1.0, users had limited interaction and mostly consumed information from static websites controlled by a few companies. Web 2.0, however, transformed this dynamic by empowering users to participate actively in the digital world. Platforms like Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter enable people to generate their own content, interact with others, and have a direct influence on the online landscape.
This participatory and collaborative nature of Web 2.0 represents a significant departure from the passive consumption of Web 1.0. Users now have more control and can engage directly with content and each other, creating a more interactive and connected online experience. This active engagement in creating and owning content is expected to be taken even further with the advent of Web 3.0.
Web 3.0 Benefits
Web 3.0 offers significant advantages, with the greatest being the immense freedom it grants to individual users. Unlike the current internet, many processes will no longer be controlled by large companies but will occur through alternative platforms and decentralized data networks.
One of the main goals of Web 3.0 is to democratize the internet, giving equal rights to everyone and allowing decisions to be made based on majority consensus. In a decentralized web, every user can help shape the internet, provided they have the necessary technical skills.
Here are some other benefits of Web 3.0:
- Automatic Access: Everyone on the network can use the services without needing explicit permission.
- Less Censorship: With no centralized management in applications, there will be more freedom and less censorship of user contributions.
- Direct Payments: Users can make direct payments without intermediaries.
- Universal Programmability: The internet will be more programmable, allowing for a wide range of applications.
- Decentralized Interaction: User interactions will increase and become more decentralized.
- Monetization Opportunities: It will be easier to monetize online presence for both application operators and users.
In simple terms, Web 3.0 means no censorship of content or users and no need for personal data in transactions, promoting decentralized finance (DeFi). Web 3.0 servers, protected by decentralized networks running in the background, promise greater security. By not sharing personal data for payments, users minimize the risk of data theft.
Overall, Web 3.0 promises both freedom and security, offering a new era of the internet where users have more control and protection.
Web 3.0 Risks
While Web 3.0 offers many exciting opportunities, it also presents several risks and challenges. Ensuring a transparent and secure environment will be more difficult. Absolute freedom, though appealing, poses challenges, particularly in areas like law enforcement.
One major risk is the difficulty in maintaining security for individuals. With decentralized control, addressing issues such as harassment, bullying, and fraud becomes more challenging. Previously, companies handled these issues to some extent, but in Web 3.0, the responsibility would fall on individuals.
The excitement surrounding Web 3.0 also carries the risk of a potential bubble. The sudden surge in interest and investment could lead to inflated expectations, which might not be sustainable if the necessary technologies and infrastructures are not fully developed.
Currently, much investment is directed towards the idea of the Semantic Web, but many essential technologies and infrastructures are still in development. As a result, Web 3.0 is not yet ready for widespread adoption, and there is a risk that it may not meet the high expectations set for it.
Web 3.0: FAQ
Is Web 3.0 the future?
Yes, Web 3.0 is considered the future of the Internet. It aims to create a more decentralized, user-centric, and secure online ecosystem. By emphasizing user empowerment, data privacy, and decentralized applications, Web 3.0 aspires to fulfill the original ideals of a free and open web.
Who started Web 3.0?
The term “Web 3.0” was coined by Gavin Wood in 2014, marking the beginning of a new era for the internet. However, the foundational principles align closely with the vision of Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, who has always advocated for a more decentralized and user-focused Internet.
Does Web 3.0 exist yet?
Web 3.0 is currently in its early stages. While many foundational technologies and principles have been established, full development and widespread adoption are still in progress. It will take time for Web 3.0 to become the dominant form of the Internet.
How to make money in Web 3.0?
One primary way to make money in Web 3.0 is by investing in crypto projects. As the decentralized web grows, numerous promising projects are emerging. For more insights and recommendations, you can refer to articles such as “Best Crypto to Buy Now.”
What is the difference between Web 3.0 and Metaverse?
Web 3.0 refers to the next iteration of the internet, focused on decentralization and user empowerment, aiming to reduce censorship and data misuse. The metaverse, on the other hand, is a network of interconnected virtual worlds where users interact through digital avatars, engaging in various activities and owning unique digital assets like virtual land or items. While Virtual Reality (VR) is crucial for an immersive metaverse experience, Web 3.0 does not inherently require VR and currently operates mostly on PCs and mobile devices. However, many metaverse projects will integrate Web 3.0 technologies in the future.
Is Web 3.0 a blockchain platform or a cryptocurrency?
No, Web 3.0 is not a blockchain platform or a cryptocurrency. While it is closely connected to blockchain technology and often involves the use of cryptocurrency wallets in browsers and online platforms, Web 3.0 encompasses much more. It aims to change how users interact with the web, create and manage digital content, and handle their online identities.
What is Web 4.0?
Web 4.0 is a speculative concept and has not been clearly defined yet. While Web 3.0 focuses on decentralization and user empowerment, Web 4.0 remains a theoretical discussion. It is expected that Web 4.0, if it emerges, will build on the foundations of Web 3.0, potentially incorporating more advanced technologies and concepts that are not yet fully understood.
Disclaimer:
Please note that this information is not financial or investment advice. The contents reflect the author’s opinion only and should not be considered trading or investment recommendations. We do not guarantee the completeness, reliability, or accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile and can experience arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or crypto user should research multiple viewpoints and be aware of local regulations before making any investments.


