So, you know how cryptocurrency isn’t as mysterious as it was five years back, but loads of folks still don’t quite get it? With all the buzz about stuff like NFTs, DeFi, and the metaverse, crypto and blockchain are like the cool kids on the block now. But tons of folks still see it as just a gamble.
As someone who uses crypto myself, I’m always getting asked, “What is cryptocurrency?” Usually, I just say, “It’s like money, but without banks or governments — totally private and owned by the users.” But there’s a whole deeper explanation too. In this article, I’ll try to break down crypto and show how handy it really is. Let’s go!
How Does Cryptocurrency Work? Crypto Explained
Cryptocurrency is basically a code, and it only exists online. Each coin is protected from cheats using something called a hash.
The big difference from regular money is that cryptocurrencies aren’t controlled by any one central authority. There’s no big bank or group of folks who can just change the rules whenever they feel like it. Instead, there’s this network of computers called nodes. Each person involved runs some software that lets them chat with others and swap info.
Think of it like this: in a regular bank setup, everyone has to talk through a central server. But with crypto, it’s more like a big web where all the nodes connect directly to each other and share info without anyone being in charge.

Cryptocurrency is like computer code, it only exists online and it’s protected from scams by something called a hash. All the digital money lives in the network, there’s no offline version.
Now, unlike regular money that’s controlled by banks or governments, cryptocurrencies are decentralized. There’s no one big authority that can change the rules without everyone’s say-so. Instead, there are these computer networks called nodes. Each person involved runs software that lets them talk to others and swap info.
In a regular banking setup, everyone has to go through a central server to interact. But with crypto, it’s more like a big web where all the nodes connect directly and share info without any one boss.
This decentralized setup makes it super hard to shut down or censor crypto networks. Unlike traditional systems where just hitting the main server can cause chaos, with crypto, even if you mess with one part, the rest keeps chugging along. Plus, if a bank loses its data, it’s a real headache to figure out who has what money.
In cryptocurrency, every node keeps a copy of the database, which is basically like a digital record book called the blockchain. Each node acts like its own little server. So, even if some nodes go offline, the others can still keep things going by sharing info.
That’s why cryptocurrencies never sleep – they’re up and running all day, every day. They let you move money around the world without needing middlemen. That’s why we say they’re free from restrictions – anyone with internet access can send money wherever they need to.
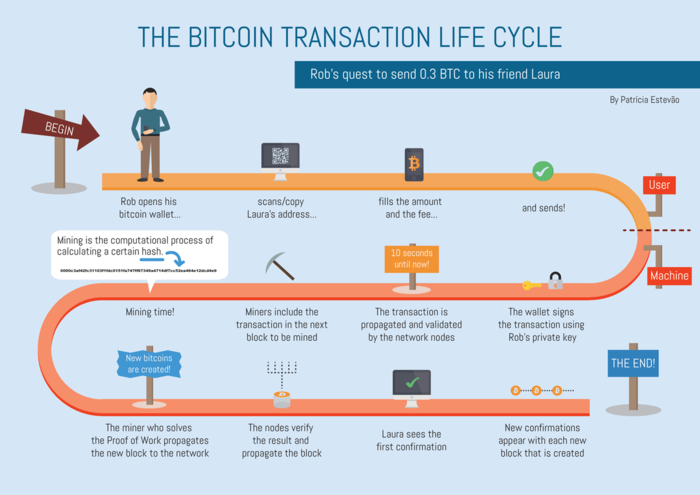
Let’s look at the example. Here we have two people with mobile wallets. Alice sends 1 Bitcoin to Bob using their mobile wallets:
Let’s break down how Alice sends 1 Bitcoin to Bob using their mobile wallets:
- Alice initiates a transaction, specifying that she wants to send 1 Bitcoin to Bob’s wallet. This transaction includes the amount, Bob’s Bitcoin address, and a digital signature created using Alice’s private key.
- Nodes in the network verify if Alice indeed has 1 Bitcoin and if the transaction is valid, which means it includes Alice’s digital signature.
- After verification, every node updates its version of the blockchain by adding information about Alice’s transaction. The blockchain keeps records of all transactions ever made.
- Both Alice and Bob use wallet software to interact with the network. This software handles keys and tracks incoming and outgoing transactions. Once the transaction is confirmed, Bob receives a notification about the money he received, and Alice gets confirmation that her transaction went through.
Types of Cryptocurrency
Besides Bitcoin, there are tons of other virtual currencies out there, known as “altcoins” or alternative coins. You’ve got a whole bunch of them flooding the market, like Ethereum, Litecoin, Polkadot, and many more.
Now, some coins are tied to regular money or even gold. These are called stablecoins. One big example is Tether (USDT), which sticks to the value of the US dollar. Another one is the USD Coin (USDC). There’s also STASIS EURO (EURS) tied to the euro, and BiLira (TRYB) tied to the Turkish lira. And then you’ve got PAX Gold, which is backed by actual gold bars stored in Brink’s gold vaults.
Another type of cryptocurrency is a token. Tokens are different from regular cryptocurrencies because they’re meant to represent a digital balance in a specific asset. We’ll dive deeper into the difference between coins and tokens later on.
Then there are NFTs, which stand for non-fungible tokens. They’re not exactly cryptocurrencies but more like digital versions of assets, whether they’re physical or not. NFTs are recorded on the public ledger, and blockchain, and they can represent anything from artwork to real estate or even a tweet.
How to Use Cryptocurrency? Crypto Use Cases
Cryptocurrencies are super popular because they’re decentralized, meaning no single authority controls them. Plus, lots of folks beyond just crypto enthusiasts are getting on board, which opens up a bunch of different ways to use them. Here are some of the main ways people use cryptocurrency:
Digital Payments
Cryptocurrencies are great for making day-to-day transactions, although volatility is still an important factor explaining why most merchants do not accept them as a payment method. However, as time goes by, more and more merchants are starting to support digital currency.
Cryptocurrency transactions are much easier now than they used to be a few years ago. New technologies, such as layer 2, or the transformation of the Ethereum blockchain from the proof-of-work consensus mechanism to the proof-of-stake one, have provided both merchants and regular users with cheap and efficient ways to transfer digital assets.
Transactions
Apart from just being a way to pay for stuff, crypto is handy for transferring money too. Unlike regular money that’s tied up in local laws and rules, Bitcoin and other altcoins can move around cheaply and quickly. This makes them a great option for sending money, especially to places with less advanced banking systems, where traditional bank transfers can be slow and pricey.
Crypto isn’t just about buying stuff or transferring money – it’s also a whole new world for trading. Whether you’re just starting out or you’re a pro, crypto trading offers a fresh way to diversify your investments.
While folks are familiar with trading stocks, forex, and commodities, diving into crypto trading lets you expand your portfolio even further. And it’s not just about basic buying and selling – now you’ve got all these extra features like futures, margin trading, and more popping up on lots of platforms. So, there are plenty of ways to get involved and grow your money in the crypto world.
Anti-Corruption and Anti-Poverty Tool
Cryptocurrencies play a crucial role in giving financial access to about 40% of people globally, especially those without bank accounts in developing nations like Myanmar, where this number hits a staggering 95%. Challenges like distant bank locations, lack of assets, and documentation hurdles often lock people out of traditional banking.
By leveraging cryptocurrencies and blockchain tech, folks gain access to financial services, enabling them to save, borrow, shop online, and invest, which was out of reach before. This can significantly chip away at poverty.
Plus, unlike traditional banking where authorities can track, freeze, or block transactions – like what happened with WikiLeaks – cryptocurrencies offer more freedom. They can also serve as a shield against hyperinflation, like what hit Zimbabwe in 2008, where prices doubled every day. Cryptos don’t get caught up in such market chaos.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, is a hot new trend that’s catching on fast. These platforms use smart contracts on blockchain networks, mostly Ethereum, to build financial systems like loans, interest accounts, and exchanges – all without the need for middlemen. It’s like recreating traditional finance but in a more direct, peer-to-peer way.
Privacy and Censorship Resistance
Some cryptocurrencies like Monero and Zcash offer enhanced privacy features, making transactions completely untraceable. This can be crucial for individuals in regions with strict financial censorship or those who prioritize financial privacy.
Store of Value
Bitcoin, in particular, is often referred to as “digital gold” due to its limited supply and decentralized nature, with some seeing it as a hedge against inflation and a store of value similar to precious metals.
Tokenization of Assets
Cryptocurrencies can represent other forms of value. For instance, tokens can be issued to represent shares in a company, real estate, or any other form of real-world asset, making asset ownership and transfer more fluid.
Supply Chain and Authenticity Tracking
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology can revolutionize supply chains by providing transparent and unchangeable records. This ensures the authenticity of products, tracking their journey from creation to the hands of consumers.
Fundraising and Crowdsales
New methods of fundraising like Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Security Token Offerings (STOs) have become popular alternatives to traditional investment avenues. These token-based fundraising methods offer innovative ways for projects to raise funds and engage with investors.
Gaming and Virtual Goods
Cryptocurrencies have made their mark in the gaming industry, enabling players to purchase in-game items, land, or characters using digital currencies. Some games have even built their economies around cryptocurrencies, providing players with new opportunities for virtual asset ownership and trading.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Cryptocurrencies
Here’s a breakdown of the advantages and disadvantages of cryptocurrencies, followed by a question about their legality:
Advantages:
- Accessibility: Cryptocurrencies offer round-the-clock access to funds without the risk of freezing accounts.
- Anonymity: Transactions are difficult to trace back to individuals, providing a level of privacy not seen in traditional banking.
- Limited Supply: Most cryptocurrencies have a finite supply, attracting investors and mitigating inflation risks.
- Decentralization: Cryptocurrencies operate independently of central authorities, appealing to those wary of government control.
- Low Transaction Fees: Transferring funds across borders incurs minimal fees compared to traditional banking methods.
- Minimal Requirements: Users only need a digital wallet to start using cryptocurrencies, without the need for personal information or traditional banking services.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of Government Trust: Many governments do not recognize cryptocurrencies as legitimate assets, leading to restrictions and prohibitions in some jurisdictions.
- Irreversible Transactions: Due to blockchain’s immutable nature, refunds are challenging, and transactions cannot be reversed.
- Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices are highly unpredictable, leading to significant fluctuations and potential financial risks for investors.
- Risk of Losing Private Keys: If users lose their private keys, access to their cryptocurrency holdings becomes impossible.
- Lack of Regulatory Protection: Cryptocurrency users bear personal responsibility for securing their funds, with limited recourse in case of theft or loss.
Are Cryptocurrencies Legal?
Certainly! I’d be happy to help create a table on governments’ relations to Bitcoin. Could you please provide the specific statements or categories you’d like to include in the table? For example, you might want to categorize countries as “Legal,” “Regulated,” “Restricted,” or “Banned.” Additionally, if you have a list of countries you’d like to include or any specific criteria, please let me know!
| Illegal | Legal | Undefined* |
| Algeria | Nigeria | Namibia |
| Egypt | Mauritius | Canada |
| Morocco | Angola | Columbia |
| Bolivia | South Africa | Russia |
| Afganistan | The USA | Saudi Arabia |
| Nepal | El Salvador | Jordan |
| China | Mexico | Taiwan |
| Bangladesh | Costa Rica | Cambodia |
| Nicaragua | Vietnam | |
| Jamaica | Tanzania | |
| Argentina | Zimbabwe | |
| Brazil | Ecuador | |
| Chile | UAE | |
| Venezuela | Turkey | |
| Uzbekistan | Thailand | |
| Kyrgyzstan | ||
| Cyprus | ||
| Israel | ||
| Lebanon | ||
| India | ||
| Hong Kong | ||
| Japan | ||
| South Korea | ||
| Malaysia | ||
| Philippines | ||
| Singapore | ||
| Brunei | ||
| The UK | ||
| Central African Republic | ||
| Australia |
*Undefined mostly means that cryptocurrencies are not recommended for use by the government but are not prohibited. Please check the rules and regulations in your country before buying or trading any cryptocurrencies.
*Please note that this table is for informational purposes only, and regulations may change over time. It’s essential to check the rules and regulations in your country before buying or trading any cryptocurrencies.
Differences between coins and tokens:
Coins:
- Coins are standalone cryptocurrencies with their own blockchain.
- They function as full-fledged digital currencies and can be used for various purposes.
- Examples include Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
Tokens:
- Tokens are internal units within the blockchain of a specific cryptocurrency.
- They are designed for specific functions within a particular blockchain ecosystem.
- Tokens do not have their own blockchain and are not considered independent cryptocurrencies.
- Examples include ERC-20 tokens on the Ethereum blockchain, which are used for various purposes such as utility, governance, or representing assets.
In essence, coins are like digital money with their own blockchain, while tokens are specific units within a blockchain designed for particular functions.
Read more about the differences between token and coin in our article.
Should You Invest In Cryptocurrencies?
Before diving into cryptocurrency investment, here are some important tips to consider:
- Do Your Own Research (DYOR): Take the time to study the market thoroughly before investing in any cryptocurrency. Understand the technology, the project’s goals, and its potential for growth. Remember, there are always risks involved, so knowledge is your best defense.
- Timing is Key: Unlike the stock market, cryptocurrency prices can fluctuate rapidly. Don’t rush to buy or sell based on short-term price movements. Instead, monitor the market closely and wait for the right moment to make your move.
- No Guarantees: Just because a cryptocurrency has been rising in value doesn’t mean it will continue to do so. Market dynamics can change quickly, and there are no guarantees of profits. Always invest with caution and be prepared for potential losses.
- Patience is a Virtue: Good investment opportunities don’t come around every day. Take your time to analyze the market, identify promising projects, and wait for the right opportunity to present itself. Patience is key to successful long-term investing.
Remember, investing in cryptocurrencies carries inherent risks, and it’s essential to approach it with caution and diligence. If you’re ready to start your investment journey, Changelly is here to provide you with the best cryptocurrency purchase rates.
Here are some of the best cryptocurrencies you can buy now.
FAQ
How long do cryptocurrency transactions take?
Cryptocurrency transactions can vary in speed depending on factors like market congestion and transaction fees. For instance, Bitcoin transactions may take 10 minutes to an hour or longer, while others can be almost instant. Additional processing times may apply depending on financial institutions or exchanges.
Is Bitcoin a digital currency?
Yes, Bitcoin is a digital currency. It was the first cryptocurrency introduced and operates on a decentralized network using blockchain technology, which securely records transactions.
What is the difference between centralized and decentralized cryptocurrency exchanges?
Centralized exchanges (CEXs) are run by companies and act as intermediaries, holding user funds. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) operate without a central authority, facilitating direct transactions between users using smart contracts.
Is blockchain technology only used for cryptocurrency?
No, blockchain has applications beyond cryptocurrency. It can record transactions in various industries, offering transparency and efficiency without centralized oversight.
Are NFTs cryptocurrency?
NFTs are not traditional cryptocurrencies. While both use blockchain technology, NFTs represent unique digital assets or proofs of authenticity, unlike cryptocurrencies designed for exchange or store of value.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability, and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.


